Thermoacoustic cooling
A new heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator for waste heat recovery is studied. The system uses a gas-liquid resonator in replace of traditional gas-only resonator, to enable a lower onset temperature and better cooling performance for harvesting low-grade heat. Calculation results show that the proposed system can significantly reduce the onset temperature difference from 144.1 K to below 35.5 K. The results also represent significant increases by a factor of 5.6 in cooling power and 1.5 in efficiency from a gas-only to a gas-liquid resonator.
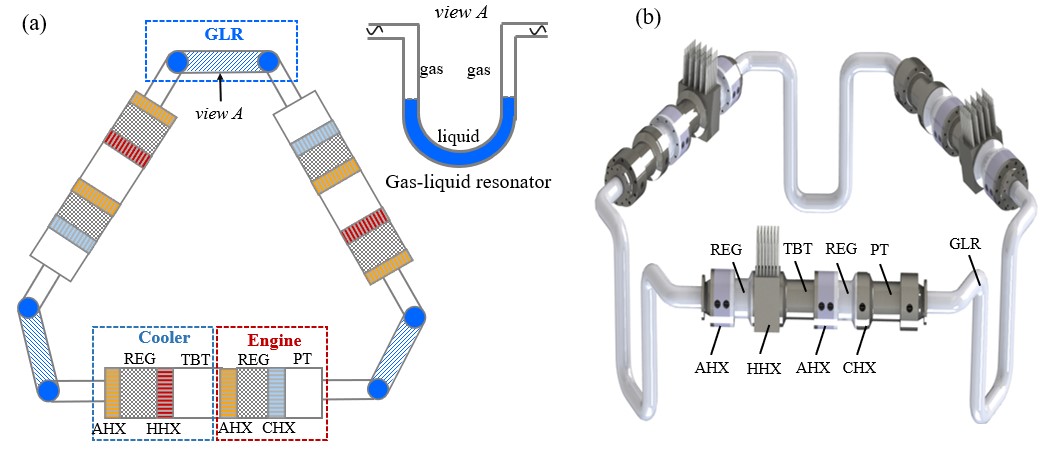
Schematics of a looped multi-stage thermoacoustically-driven refrigerator using gas-liquid resonators for recovering low-grade heat.
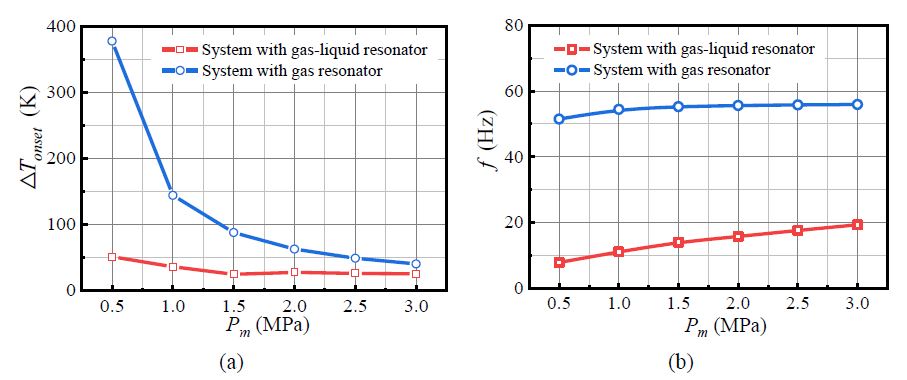
Comparison of (a) onset temperature difference (b) working frequency between thermoacoustically-driven refrigerators with gas-only resonators and gas-liquid resonators.
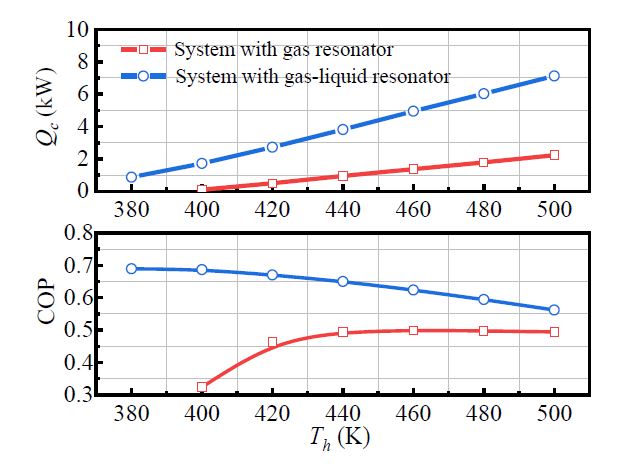
Calculated performance of systems with the gas resonator and with the gas-liquid resonator.
Further details in: J. Xu, E. Luo, S. Hochgreb. Study on a heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator for low-grade heat recovery. Applied Energy 2020; 271: 115167.
The material has been highlighted in Advances in Enginering.