|
|
||||||||
Super Models
Members of the team are now looking at a wide variety of applications including the generic design of a Formula One racing car. The inter-component effects of making small changes in design are being examined as a series of fourth year projects. These are so popular that they are over-subscribed by a factor of four and successful students working in this area frequently go on to join Formula One design teams. Another application is modelling the new lattice heat exchanger materials being developed in the Materials Division. By modelling their flow characteristics it is hoped to optimise their design for applications such as cooling electronic components. Novel adaptive meshing techniques are now also being used to study flow of air in and out of lung alveoli and to investigate disruption of electrical current flow around a heart.
|
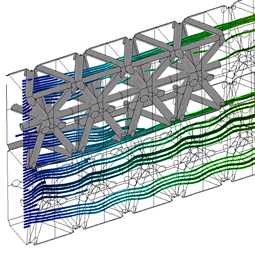
This simulation aims to investigate the heat transfer properties of a lattice material, with a fully realistic CFD geometry model. The pressure loss through the device is also investigated. The streamlines shown here illustrate the general flow pattern. Experimental data is very difficult to obtain, and the CFD is used to improve understanding for design configuration optimisation. Image generated by Will Kellar. |
|
For more information about the work of the CFD laboratory, visit their web site, or contact Dr Mark Savill - ams3@eng.cam.ac.uk.